中子照相已被广泛应用于许多学科,从物理,生命和地球科学的材料研究到工业组件和文物的无损检测。目前,大多数中子照相设备都是基于反应堆中子源和散裂中子源,它们可以提供高的中子通量和高质量的热中子束。然而,在某些情况下,人们希望拥有一个紧凑型加速器驱动的中子源(CANS)的中子照相设备,并且可以在现场使用,甚至可以移动。这意味着它的尺寸尽可能小,并且其成本尽可能低。
北京大学中子照相装置(PKUNITY)是基于RFQ加速器驱动的紧凑型中子源,目前已经在北京大学建造和调试完成。该项目建成了我国首台基于加速器的现场中子照相装置,系统地开展了针对碳/碳复合材料中子射线检测方法的研究,并实现了中子数字成像,获得了工程化的初步成果。在中子照相适用性研究方法、RFQ中子发生器技术、中子照相装置设计等方面具有创新性。
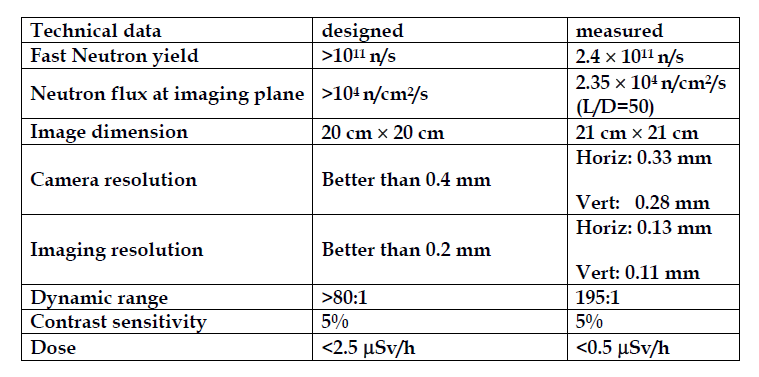
该装置基于一台强流RFQ加速器(Table 2),通过氘-铍核反应产生中子,快中子产额为2.4×1011n/s。成像平面上的热中子通量在L / D比为50时为2.35×104n/cm2/s,并且L / D比可在25-200的范围内选择,相应的n/γ比接近或高于1×1010 n/cm2/Sv。在准直器入口孔下游2m处的视野为20cm×20cm,其中热中子通量均匀性优于7%。Table 1.列出了PKUNITY的主要技术参数。
The method of neutron radiography has been widely used in many disciplines, from materials research in physical, life and earth sciences to non-destructive characterization of industrial components and artifacts of cultural heritage. Currently most of the neutron radiography facilities are based on the reactor neutron source and spallation neutron source, which can give intense neutron flux and high quality neutron radiographs. However, in some cases people would like to have a neutron radiography facility, which is based on a compact accelerator-driven neutron source (CANS), and can be used on the spot or even can be movable. That means its size is as small as possible, and its cost is as low as possible.
The Peking University Neutron Imaging Facility (PKUNIFTY), based on RFQ accelerator-driven compact neutron source, has been constructed and commissioned at Peking University. The project has built the first accelerator-based neutron radiography facility in China, systematically carried out research on neutron radiation detection methods for carbon/carbon composite materials, and realized neutron digital imaging, and obtained preliminary results of engineering. It is innovative in neutron radiography applicability research methods, RFQ neutron generator technology, and the design of neutron radiography facility.
The device is based on a high-current RFQ accelerator (Table 2). Neutrons are generated via the deuteron-beryllium reaction with a fast neutron yield of 2.4×1011n/s. The thermal neutron flux on the imaging plane is 2.35×104n/cm2/s at a nominal L/D ratio of 50, and the L/D ratio can be selectable over a range of 25-200. The corresponding n/γ ratio is close to or higher than 1×1010 n/cm2/Sv. The field of view is 20cm×20 cm at 2m downstream of the collimator entrance aperture where the thermal neutron flux uniformity is better than 7%. The main technical parameters of PKUNITY are listed in Table 1.
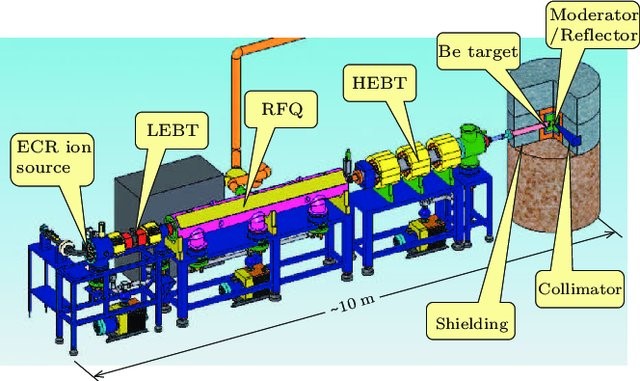
Fig 1. Outline of PKUNITY
Table 1. Technical Parameters of PKUNIFTY
PKUNITY由三个子系统组成。
(a) 加速器(Fig 2.):加速器包括ECR离子源,低能束流传输段(LEBT),RFQ腔和高能束流传输段(HEBT),出口能量2MeV,平均流强4mA。
(b) 靶-慢化剂-反射体组件(Fig 3):从Be靶发射出的快中子被慢化剂慢化,慢化剂周围的反射体将逃逸的快中子重新反射到慢化剂中,从而最终增加了热中子的通量,准直器将成形的热中子束传输到成像站。屏蔽体可以吸收从组件中逃逸出的中子和γ光子,用于人员和环境的辐射防护以及在数据收集中实现高信噪比。
(c) 成像系统:包括一个接收发射的中子并将其转换成光的闪烁屏、两个反射镜以将光线从中子束中反射出去,以及一个透镜和一个用于成像的冷却式CCD相机。
The PKUNIFTY consists of three subsystems.
(a) The accelerator (Fig 2.): the accelerator includes an ECR deuteron ion source, a low energy beam transport (LEBT), a RFQ cavity and a high energy beam transport (HEBT). It generates a deuteron beam at 2MeV with an average current of 4mA.
(b) The target-moderator-reflector assembly (Fig 3.): the fast neutrons emitted from the beryllium target are slowed down by the moderator medium. The reflector around the moderator redirects some of the escaped fast neutrons back to the moderator, thereby enhancing the eventual thermal neutron intensity. A collimator facilitates a conduit for transporting the thermal neutrons with a shaped beam profile toward the imaging station. The shielding surrounding the target, moderator, and reflector capture and/or absorb the neutrons and g-rays from escaping outside the assembly for radiation protection of personnel and the environment as well as for realizing a high signal-to-noise ratio in data collection.
(c) The imaging system: it includes a scintillation screen that accepts the transmitted neutrons and converts them into light, two mirrors to reflect the light away from the neutron beam, and a lens and a cooled CCD camera for imaging.
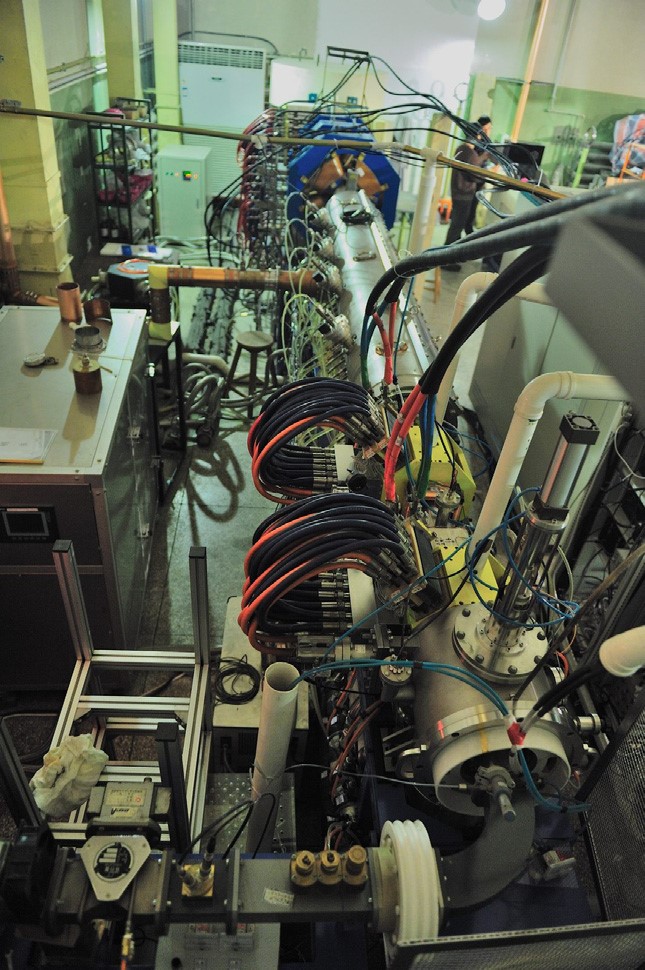
Fig 2. The RFQ accelerator of PKUNIFTY
Table 2. Key parameters of the PKUNIFTY RFQ
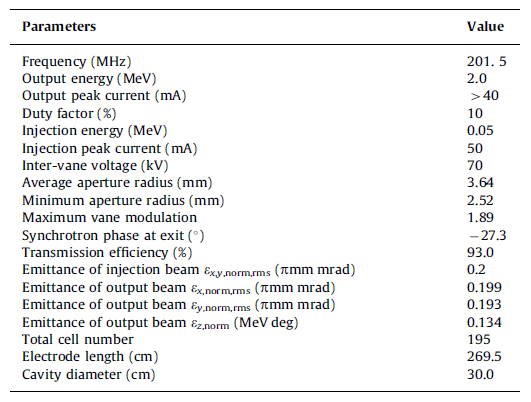
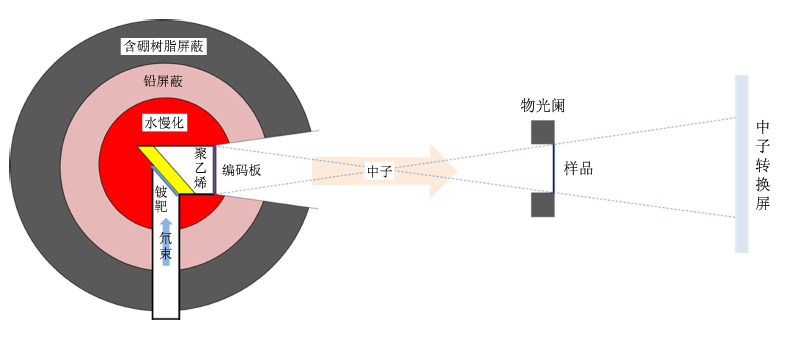
Fig 3. Experimental platform diagram.
在我们的实验中测试了如Fig 4. (a)所示的铜锁。Fig 4. (b)显示了它的中子照片,可以清楚地看到它的内部结构。然后我们注入了一些润滑油,带有油的照片Fig 4. (c)所示,图中可以识别出油分布。Fig 5.显示了其他的中子照相的实验结果。
A copper lock, shown in Fig. 4(a), was tested in our experiments. Fig. 4(b) shows its neutron radiograph, in which its inner structure can be seen clearly. Then we inserted some lubricating oil, and the radiograph with oil is shown in Fig. 4(c), in which the oil distribution can be recognized. Fig 5. Shows the neutron radiography results of some other experiments.
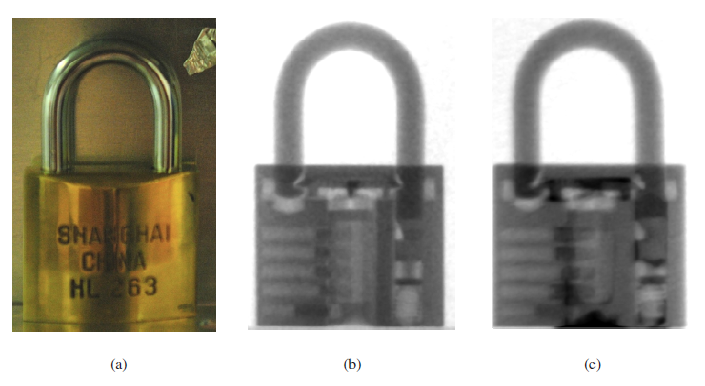
Fig 4. The photo and neutron radiographs of a copper lock. (a) photo, (b) neutron radiograph with oil, (c) neutron radiograph with filled oil.
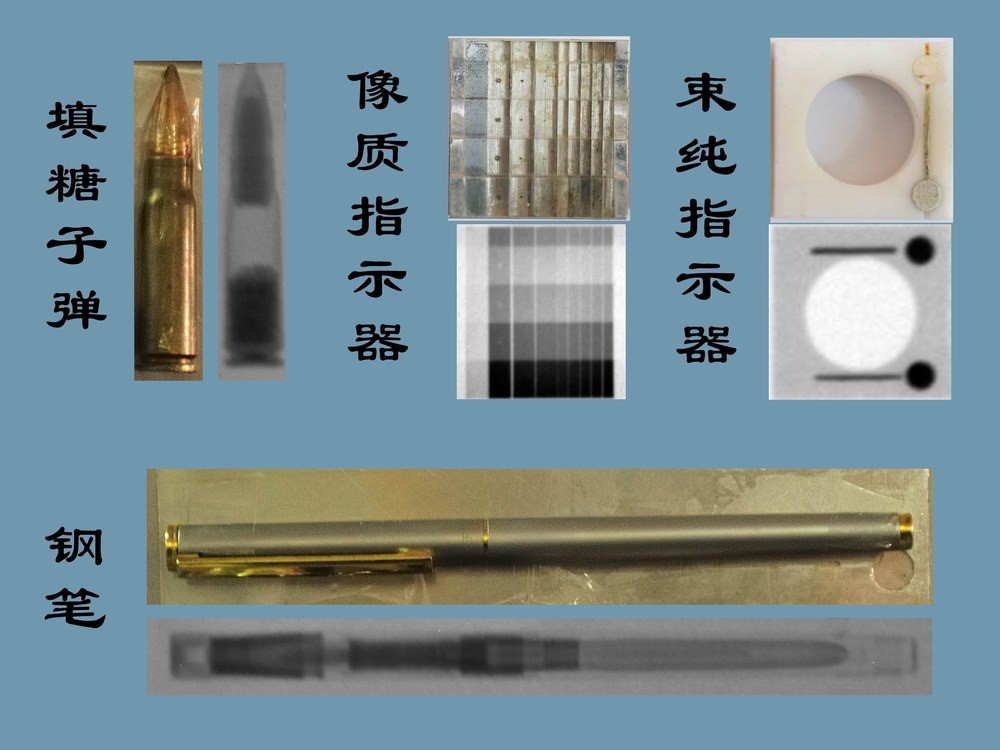
Fig 5. The neutron radiography results of other experiments.
